2021AICompetition-03
본 repo 는 mAy-I Inc. 팀으로 참가한 2021 인공지능 온라인 경진대회 중 [이미지] 운전 사고 예방을 위한 운전자 부주의 행동 검출 모델] 태스크 수행을 위한 레포지토리입니다.
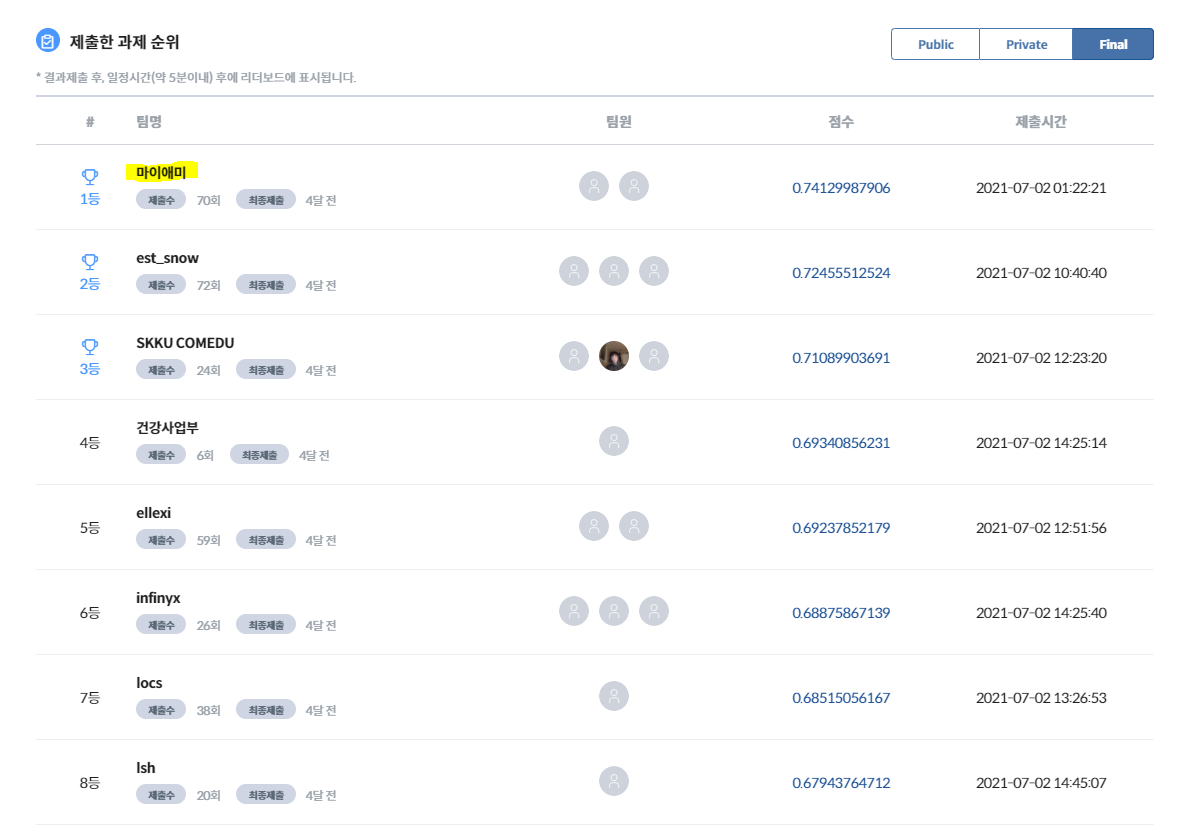
mAy-I 는 과학기술정보통신부가 주최하고 정보통신산업진흥원이 주관하는 2021 인공지능 온라인 경진대회 에 참가하여, 이미지 분야 177개 팀 중 최종 1위 를 달성하여 과학기술정보통신부장관상 을 수상하였습니다.
본 repo 는 그 중 [이미지] 운전 사고 예방을 위한 운전자 부주의 행동 검출 모델 태스크를 다루고 있으며, mAy-I 는 해당 태스크에서 Public/Private/Final 모든 데이터셋에 대해 종합 1위 를 달성하였습니다.
관련한 보다 자세한 소개는 mAy-I 테크 블로그에서 보실 수 있습니다: 2021 인공지능 온라인 경진대회 이미지 분야 1위 어떻게 했을까?
- 메이아이, ‘AI 온라인 경진대회’서 과기부 장관상 수상
- mAy-I 는 작년에도 3개 태스크에서 각각 1위, 2위, 2위를 달성하여 종합 5위에 랭크되었습니다:)
대회 중 작성하였었던 코드를 아카이빙하는 것이 목적이라, 별도의 문서화나 리팩토링을 거치지 않은 점, 양해 부탁드립니다:)
셋업
학습 및 추론을 위한 환경을 구축하는 단계입니다.
별도 셋업
별도의 환경을 위한 셋업 과정입니다. docker 가 설치되어 있고, dataset 이 알맞은 경로에 준비되어 있다면 생략할 수 있습니다.
docker 설치
본 repo 는 간편한 설치를 위해 docker 를 사용합니다. 서버에 docker 가 설치되어 있지 않은 경우 다음과 같은 방식으로 설치 가능합니다.
$ sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
$ sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-cache search docker-ce
# Message: docker-ce - Docker: the open-source application container engine
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install docker-ce
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
$ curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/gpgkey | sudo apt-key add -
$ distribution=$(. /etc/os-release;echo $ID$VERSION_ID)
$ curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/$distribution/nvidia-docker.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-docker.list
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-container-toolkit
$ sudo systemctl restart docker
도중에 sudo: unable to resolve host 에러가 나오면 링크 로 해결하면 됩니다.
데이터 다운로드 및 셋업
제공된 데이터는 다음과 같은 경로에 셋업되어야 합니다.
- train 데이터 경로:
/DATA/Final_DATA/task03_train - test 데이터 경로:
/DATA/Final_DATA/task03_test
위와 같이 셋업되어 있지 않은 경우, 제시된 데이터 파일을 다운로드 받아 /DATA/Final_DATA/ 폴더에 놓은 후, 다음의 코드로 압축을 풀어 세팅합니다.
## 기본 제공 데이터를 drowsy_face_raw 폴더에 압축 해제
$ sudo unzip /DATA/Final_DATA/task03_train.zip -d /DATA/Final_DATA/task03_train
$ sudo unzip /DATA/Final_DATA/task03_test.zip -d /DATA/Final_DATA/task03_test
## 용량이 부족하다면 .zip 파일은 삭제
$ sudo rm ../drowsy_face_raw/task03_train.zip
$ sudo rm ../drowsy_face_raw/task03_test.zip
폴더 세팅
작업 폴더를 세팅하기 위해 제출한 코드를 ~/workspace/code/2021AICompetition-03 에 세팅합니다.
혹은 다음과 같이 git 에서 가져옵니다.
$ mkdir -p ~/workspace/code
(~/workspace/code) $ git clone https://github.com/PJunhyuk/2021AICompetition-03
** 이후의 모든 코드는 특별한 언급이 없다면 current work directory(~/workspace/code/2021AICompetition-03) 하에서의 실행을 전제합니다.
docker 및 git, ffmpeg (for opencv) 세팅
여러 docker image 중 nvidia/pytorch 의 기본 이미지를 활용하였습니다. 다음과 같은 방식으로 docker 를 가져오고, 기본 package 인 git 과 ffmpeg 를 설치합니다.
- 추가 설치가 워낙 간단하여, 별도로 docker image 파일을 만들지는 않았습니다.
$ docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:20.12-py3
$ docker run --gpus all --name 2021AICompetition-03 --shm-size 8G -v ~/workspace/code:/root/workspace/code -v /DATA:/DATA -it nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:20.12-py3
# Install git & ffmpeg
# 'glib2' is a dependency of 'opencv'
# type 6-69-6
$ apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
git libxrender1 ffmpeg libglib2.0-0 && \
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
dependencies 설치
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
학습 및 추론
학습
$ python train.py
추론
$ python predict.py
코드 설명
repo 전반에 대한 상세 설명입니다.
Code file 에 대한 description
구조
Code file 은 다음과 같은 구조로 이루어져 있습니다.
~/workspace/code/2021AICompetition-03 (current work directory)
/data
drowsy_face.yaml
drowsy_face_tuning.yaml
hyp.scratch-p6.yaml
hyp.finetune.yaml
hyp.finetune-simple.yaml
/models
/hub
yolov5l6.yaml
*.py
/utils
*
.gitignore
README.md
requirements.txt
train.py
predict.py
상세 설명
-
${PROJECT}/data/drowsy_face.yaml: baseline 학습 환경에 대한 정보가 담겨 있는 파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/data/drowsy_face_tuning.yaml: fine-tuning 학습 환경에 대한 정보가 담겨 있는 파일입니다.drowsy_face.yaml파일과 train dataset 경로 부분에서만 차이가 있습니다. -
${PROJECT}/data/hyp.scratch-p6.yaml: baseline 학습에 필요한 hyperparameter 들의 정보가 담겨 있는 파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/data/hyp.finetune.yaml: fine-tuning 학습에 필요한 hyperparameter 들의 정보가 담겨 있는 파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/data/hyp.finetune-simple.yaml: fine-tuning 학습에 필요한 hyperparameter 들의 정보가 담겨 있는 파일입니다.hyp.finetune.yaml과 달리hsv_v,scale,mosaic를 사용하지 않습니다. -
${PROJECT}/models/hub/yolov5l6.yaml: 학습에 사용한 backbone 인yolov5l6에 대한 정보가 담겨 있는 파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/models/*.py: yolov5 를 기반으로 하고 있는 파일들입니다. 원본 파일들과 크게 차이가 없습니다. -
${PROJECT}/utils/*: yolov5 를 기반으로 하고 있는 파일들입니다. 원본 파일들과 크게 차이가 없습니다. -
${PROJECT}/.gitignore: GitHub 를 위한.gitignore파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/README.md: repo 전반에 대한 설명이 담겨 있는 파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/requirements.txt: dependencies 가 담겨 있는 파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/train.py: 학습에 사용하는 파일입니다. -
${PROJECT}/predictpy: 추론에 사용하는 파일입니다.
output 에 대한 description
구조
코드가 실행되면 기존 파일들 외에 다음과 같은 파일들이 생성됩니다.
~/workspace/code
/2021AICompetition-03 (current work directory)
/runs
/train
/final
/weights
last.pt
best.pt
*
/final2
/weights
last.pt
best.pt
*
/test
/final
last_predictions.json
*
/drowsy_face
/images
/train
/val
/labels
/train
/val
/drowsy_face_diet
/images
/train
/labels
/train
상세 설명
~/workspace/code/2021AICompetition-03/runs~/workspace/code/drowsy_face/:train.py를 실행하면 생성되는 폴더입니다./DATA/Final_DATA의 데이터들을 train set 과 validation set 으로 나눈 후 yolo 형식에 맞춰 저장합니다.~/workspace/code/drowsy_face_diet/:train.py를 실행하면 생성되는 폴더입니다. data imbalance 문제를 해결하기 위해/DATA/Final_DATA의 데이터들을 특정 방식에 따라 추출하여 yolo 형식에 맞춰 저장합니다.
학습에 필요한 명령어
$ python train.py
플래그
위 명령어 만으로 모든 학습 프로세스를 돌릴 수 있지만, 편의를 위해 여러 플래그들이 존재합니다. 주로 사용하는 플래그들은 다음과 같습니다.
--no_data_prepare: 이미train.py가 한 번 이상 실행되어drowsy_face와drowsy_face_diet폴더가 세팅되어 있는 경우, 본 플래그를 사용하면 data prepare 과정을 생략하고 바로 학습을 진행합니다. (default: False)--batch 4: batch size 를 조절합니다. (default: 4)--device 0: 여러 개의 GPU 가 있는 서버에서 특정 번호의 GPU 만 사용합니다. (default: '')--img 640: input image size 입니다. (default: 1280)--name final: 결과 값이 저장되는 폴더의 이름입니다. (default: exp)
적절한 사용 예시는 다음과 같습니다.
$ python train.py --epochs 2 --save_period 2 --epochs_tune 2 --save_period_tune 2
$ python train.py --no_data_prepare --device 0 --batch 4 --img 640 --epochs 1 --save_period 1 --epoch_parts 300 --epochs_tune 1 --epoch_parts_tune 1000 --save_period_tune 1
학습시간
V100 환경에서 총 26시간 정도가 소요됩니다. 세부 구성은 다음과 같습니다.
- baseline train 에 21.5시간 정도가 소요됩니다. (300 epochs completed in 21.028 hours.)
- 1 epoch 학습하는데에 4분 10초 정도 소요됩니다.
- 학습이 끝난 후 /drowsy_face/val 에 대해 validation 을 진행합니다. 6분 정도 소요됩니다.
- fine-tuning 에 4.5시간 정도가 소요됩니다. (50 epochs completed in 4.295 hours.)
- 1 epoch 학습하는데에 5분 정도 소요됩니다.
- 학습이 끝난 후 /drowsy_face/val 에 대해 validation 을 진행합니다. 6분 정도 소요됩니다.
학습/추론 속도 체크를 위해 NAVER CLOUD PLATFORM 의 GPU Server 를 생성하여 사용했습니다.
서버 스펙
- CPU: 8 vCPUs
- RAM: 90GB
- GPU: Tesla V100
- VRAM: 32GB
- OS: Ubuntu 16.04
서버 상태
# CUDA
$ nvcc --version # 10.0.130
# nvidia-driver
$ nvidia-smi # 418.67, Tesla V100-SXM2..., 32480MiB
# Ubuntu
$ lsb_release -a # Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS
학습 과정
위 명령어를 통해 수행되는 전체 학습 과정은 크게 3개의 단계로 이루어져 있습니다.
1. data_prepare
/DATA/Final_DATA 를 yolo 형태의 data 로 변환하는 과정입니다.
-
원본 data 는 data imbalance 문제가 심각하여, 그대로 학습하면 적은 개수의 class 들이 잘 학습되지 않습니다. 때문에 이러한 부분을 보정할 수 있도록 데이터를 추출하여 drowsy_face_diet/train 을 생성합니다.
-
drowsy_face_diet/train 을 생성하는 알고리즘은 다음과 같습니다.
- cigar 가 있거나 phone 이 있으면 drowsy_face_diet/train 에 넣습니다.
- eye_closed 와 mouth_closed 가 동시에 있으면 drowsy_face_diet/train 에 넣습니다.
- eye_closed 와 mouth_opened 가 동시에 있으면 drowsy_face_diet/train 에 넣습니다.
- mouth_opened 가 있는 이미지 중 1/3 을 drowsy_face_diet/train 에 넣습니다.
-
전체 train data 중 random 하게 20000개를 추출하여 drowsy_face/val 에 저장합니다. 남은 data 들은 drowsy_face/train 에 저장합니다.
-
이 과정을 통해 생성된 셋들의 class 별 분포는 다음과 같습니다.
generate raw_train.json, raw_val.json
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 273224/273224 [02:17<00:00, 1991.69it/s]
generate drowsy_face/train, drowsy_face/val
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 20000/20000 [00:08<00:00, 2485.50it/s]
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 253224/253224 [01:47<00:00, 2346.73it/s]
generate diet_train.json
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 273224/273224 [00:00<00:00, 543536.13it/s]
generate drowsy_face_diet/train
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 56747/56747 [00:27<00:00, 2091.26it/s]
count classes
diet_train.json
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 56747/56747 [00:00<00:00, 500054.98it/s]
{'eye_opened': 61941, 'eye_closed': 47630, 'mouth_opened': 23254, 'mouth_closed': 25658, 'face': 56738, 'phone': 12687, 'cigar': 11370}
raw_train.json
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 253224/253224 [00:00<00:00, 619673.71it/s]
{'eye_opened': 419135, 'eye_closed': 74551, 'mouth_opened': 35233, 'mouth_closed': 127282, 'face': 253167, 'phone': 11792, 'cigar': 10499}
raw_val.json
100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 20000/20000 [00:00<00:00, 449781.67it/s]
{'eye_opened': 32994, 'eye_closed': 5975, 'mouth_opened': 2823, 'mouth_closed': 9851, 'face': 19997, 'phone': 895, 'cigar': 871}
2. baseline 학습
drowsy_face_diet/train 을 학습합니다.
- 300 epoch 학습하며, hyp.scratch-p6.yaml 과 drowsy_face.yaml 을 사용합니다.
- 모든 train set 을 학습하면 시간이 너무 오래 걸리기 때문에, RandomSampler 를 사용하여 전체 데이터셋 중 일부만 사용합니다. 해당 부분은 epoch_parts 라는 변수로 관리되며, default 값은 15 로, 전체 데이터셋을 매 epoch 마다 랜덤하게 15등분하여 그 중 첫 번째 셋을 사용합니다.
- 300 epoch 학습이 끝난 후 drowsy_face/val 에 대해 validation 을 수행합니다.
3. fine-tuning 학습
위 baseline 과정을 거치면 수가 적은 phone 과 cigar 과 같이 개수가 적은 class 들에 대해서는 높은 성능을 보여주나, face 와 같이 개수가 많은 class 들에 대해서는 상대적으로 낮은 성능을 보여줍니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 제공된 데이터셋과 class 분포가 같은 drowsy_face/train 을 사용하여 fine-tuning 합니다.
- 50 epoch 학습하며, hyp.finetune-simple.yaml 과 drowsy_face_tuning.yaml 을 사용합니다.
- 마찬가지로 RandomSampler 를 사용합니다. 해당 부분은 epoch_parts_tune 이라는 변수로 관리되며, default 값은 50 입니다.
- 50 epoch fine-tuning 이 끝난 후 drowsy_face/val 에 대해 validation 을 수행합니다.
추론 결과
위 과정은 baseline 학습과 fine-tuning 을 동시에 진행합니다. default 설정으로 새로운 환경에서 그대로 실행할 경우, 각각의 weight 는 다음의 경로에 저장됩니다.
- baseline:
runs/train/final/weights/last.pt - fine-tuning:
runs/train/final2/weights/last.pt
추론에 필요한 명령어
$ python predict.py
현재는 사전에 학습된 weights/weights_baseline.pt 와 weights/weights_tuned.pt 를 사용하여 추론을 진행하도록 하드코딩 되어있습니다. 만약 학습으로 얻은 새로운 weight 파일으로 추론을 진행하고 싶다면 다음의 명령어를 사용합니다.
$ python predict.py --weights runs/train/final/weights/last.pt runs/train/final2/weights/last.pt
추론 시간
V100 환경에서 ensemble 기준 총 1시간 정도가 소요됩니다.
추론 과정
학습 과정을 통해 생성된 2개의 weight 를 사용하여 ensemble 을 진행합니다.
추론 결과
추론 결과는 runs/test/final 경로 아래에 저장됩니다. 최종 제출 파일은 폴더 내의 last_predictions.json 에 저장됩니다.
Reproducibility
본 repo 에서는 다양한 방법으로 Reproducibility 를 제어하고 있습니다.
- 우선
train.py에서__main__함수가 시작된 직후 다음과 같은 방식으로 Reproducibility 를 제어합니다.
# Reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(opt.random_seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(opt.random_seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(opt.random_seed) # if use multi-GPU
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
np.random.seed(opt.random_seed)
random.seed(opt.random_seed)
- 기본적으로도
utils/general.py에서init_seeds함수를 통해 Reproducibility 를 제어합니다.
def init_seeds(seed=0):
# Initialize random number generator (RNG) seeds
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
init_torch_seeds(seed)
그러나 PyTorch 는 공식적으로 완벽히 Reproducibility 를 제어할 수 없습니다. 대표적으로 CUDA 함수를 사용하는 PyTorch 함수들 중 nondeterministic 한 함수들이 존재합니다. 본 repo 는 이 중 불가피하게 torch.nn.funcional.interpolate() 를 사용하고 있어, 완벽한 Reproducibility 제어가 불가합니다.
실제로 매 iter 마다 loss 를 찍어본 결과, 초반 1-20 iter 정도는 모든 loss 가 같게 나왔지만, 어느 순간부터 obj loss 가 다르게 찍히기 시작하고, 이걸 시작으로 다른 loss 들도 다르게 계산되는 모습을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
- 위에 언급한
torch.nn.funcional.interpolate()함수 혹은 obj loss 를 계산하는 과정에서 연산되는bcewithlogitsloss에서 Reproducibility 가 깨지는 것으로 추정됩니다.
때문에 본 repo 에서는 완벽한 Reproducibility 가 구현되어 있지 않습니다.
다만, 서로 다른 서버 환경에서 본 repo 의 설정대로 학습 및 추론을 진행하여 제출해 본 결과, Public testset 에 대해 각각 0.7459674232 (best, 66번째 submission) , 0.7378836101 (65번째 submission) 0.7320975839 (61번째 submission) 의 결과를 얻을 수 있었고, 해당 결과는 모두 리더보드 기준 2등에 위치한 est_snow 팀의 0.732055294 보다 높아, 순위에는 영향을 주지 않을 것으로 예상됩니다.