Coral PoseNet
Pose estimation refers to computer vision techniques that detect human figures in images and video, so that one could determine, for example, where someone’s elbow, shoulder or foot show up in an image. PoseNet does not recognize who is in an image, it is simply estimating where key body joints are.
This repo contains a set of PoseNet models that are quantized and optimized for use on Coral's Edge TPU, together with some example code to shows how to run it on a camera stream.
Why PoseNet ?
Pose estimation has many uses, from interactive installations that react to the body to augmented reality, animation, fitness uses, and more. We hope the accessibility of this model inspires more developers and makers to experiment and apply pose detection to their own unique projects, to demonstrate how machine learning can be deployed in ways that are anonymous and private.
How does it work ?
At a high level pose estimation happens in two phases:
-
An input RGB image is fed through a convolutional neural network. In our case this is a MobileNet V1 architecture. Instead of a classification head however, there is a specialized head which produces a set of heatmaps (one for each kind of key point) and some offset maps. This step runs on the EdgeTPU. The results are then fed into step 2)
-
A special multi-pose decoding algorithm is used to decode poses, pose confidence scores, keypoint positions, and keypoint confidence scores. Note that unlike in the TensorflowJS version we have created a custom OP in Tensorflow Lite and appended it to the network graph itself. This CustomOP does the decoding (on the CPU) as a post processing step. The advantage is that we don't have to deal with the heatmaps directly and when we then call this network through the Coral Python API we simply get a series of keypoints from the network.
If you're interested in the gory details of the decoding algorithm and how PoseNet works under the hood, I recommend you take a look at the original research paper or this medium post whihch describes the raw heatmaps produced by the convolutional model.
Important concepts
Pose: at the highest level, PoseNet will return a pose object that contains a list of keypoints and an instance-level confidence score for each detected person.
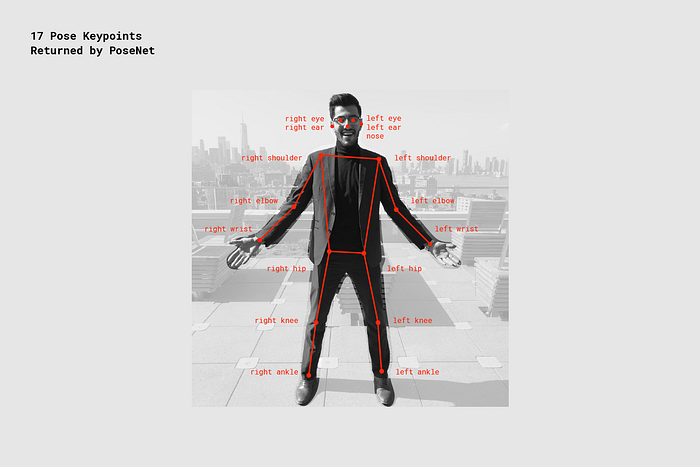
Keypoint: a part of a person’s pose that is estimated, such as the nose, right ear, left knee, right foot, etc. It contains both a position and a keypoint confidence score. PoseNet currently detects 17 keypoints illustrated in the following diagram:
Keypoint Confidence Score: this determines the confidence that an estimated keypoint position is accurate. It ranges between 0.0 and 1.0. It can be used to hide keypoints that are not deemed strong enough.
Keypoint Position: 2D x and y coordinates in the original input image where a keypoint has been detected.
Examples in this repo
NOTE: PoseNet relies on the latest Pycoral API, tflite_runtime API, and libedgetpu1-std or libedgetpu1-max:
- For pycoral
- For tflite_runtime
- For libedgetpu, please install the debian package or shared libraries. You can use either Max or Standard clock speed (these only apply for USB devices).
Please also update your system before running these examples. For more information on updating see:
- For Coral DevBoard
- For USB Accelerator
To install all other requirements for third party libraries, simply run
sh install_requirements.sh
simple_pose.py
A minimal example that simply downloads an image, and prints the pose keypoints.
python3 simple_pose.py
pose_camera.py
A camera example that streams the camera image through posenet and draws the pose on top as an overlay. This is a great first example to run to familiarize yourself with the network and its outputs.
Run a simple demo like this:
python3 pose_camera.py
If the camera and monitor are both facing you, consider adding the --mirror flag:
python3 pose_camera.py --mirror
In this repo we have included 3 posenet model files for differnet input resolutions. The larger resolutions are slower of course, but allow a wider field of view, or further-away poses to be processed correctly.
posenet_mobilenet_v1_075_721_1281_quant_decoder_edgetpu.tflite
posenet_mobilenet_v1_075_481_641_quant_decoder_edgetpu.tflite
posenet_mobilenet_v1_075_353_481_quant_decoder_edgetpu.tflite
You can change the camera resolution by using the --res parameter:
python3 pose_camera.py --res 480x360 # fast but low res
python3 pose_camera.py --res 640x480 # default
python3 pose_camera.py --res 1280x720 # slower but high res
anonymizer.py
A fun little app that demonstrates how Coral and PoseNet can be used to analyze human behavior in an anonymous and privacy-preserving way.
Posenet converts an image of a human into a mere skeleton which captures its position and movement over time, but discards any precisely identifying features and the original camera image. Because Coral devices run all the image analysis locally, the actual image is never streamed anywhere and is immediately discarded. The poses can be safely stored or analysed.
For example a store owner may want to study the bahavior of customers as they move through the store, in order to optimize flow and improve product placement. A museum may want to track which areas are most busy, at which times such as to give guidance which exhibits may currently have the shortest waiting times.
With Coral this is possible without recording anybody's image directly or streaming data to a cloud service - instead the images are immediately discarded.
The anaonymizer is a small app that demonstrates this is a fun way. To use the anonymizer set up your camera in a sturdy position. Lauch the app and walk out of the image. This demo waits until no one is in the frame, then stores the 'background' image. Now, step back in. You'll see your current pose overlayed over a static image of the background.
python3 anonymizer.py
(If the camera and monitor are both facing you, consider adding the --mirror flag.)
synthesizer.py
This demo allows people to control musical synthesizers with their arms. Up to 3 people are each assigned a different instrument and octave, and control the pitch with their right wrists and the volume with their left wrists.
You'll need to install FluidSynth and a General Midi SoundFont:
apt install fluidsynth fluid-soundfont-gm
pip3 install pyfluidsynth
Now you can run the demo like this:
python3 synthesizer.py
The PoseEngine class
The PoseEngine class (defined in pose_engine.py) allows easy access to the PoseNet network from Python, using the EdgeTPU API.
You simply initialize the class with the location of the model .tflite file and then call DetectPosesInImage, passing a numpy object that contains the image. The numpy object should be in int8, [Y,X,RGB] format.
A minimal example might be:
from tflite_runtime.interpreter import Interpreter
import os
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
from pose_engine import PoseEngine
os.system('wget https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/'
'Hindu_marriage_ceremony_offering.jpg/'
'640px-Hindu_marriage_ceremony_offering.jpg -O /tmp/couple.jpg')
pil_image = Image.open('/tmp/couple.jpg').convert('RGB')
engine = PoseEngine(
'models/mobilenet/posenet_mobilenet_v1_075_481_641_quant_decoder_edgetpu.tflite')
poses, _ = engine.DetectPosesInImage(pil_image)
for pose in poses:
if pose.score < 0.4: continue
print('\nPose Score: ', pose.score)
for label, keypoint in pose.keypoints.items():
print(' %-20s x=%-4d y=%-4d score=%.1f' %
(label, keypoint.point[0], keypoint.point[1], keypoint.score))
To try this, run
python3 simple_pose.py
And you should see an output like this:
Inference time: 14 ms
Pose Score: 0.60698134
NOSE x=211 y=152 score=1.0
LEFT_EYE x=224 y=138 score=1.0
RIGHT_EYE x=199 y=136 score=1.0
LEFT_EAR x=245 y=135 score=1.0
RIGHT_EAR x=183 y=129 score=0.8
LEFT_SHOULDER x=269 y=169 score=0.7
RIGHT_SHOULDER x=160 y=173 score=1.0
LEFT_ELBOW x=281 y=255 score=0.6
RIGHT_ELBOW x=153 y=253 score=1.0
LEFT_WRIST x=237 y=333 score=0.6
RIGHT_WRIST x=163 y=305 score=0.5
LEFT_HIP x=256 y=318 score=0.2
RIGHT_HIP x=171 y=311 score=0.2
LEFT_KNEE x=221 y=342 score=0.3
RIGHT_KNEE x=209 y=340 score=0.3
LEFT_ANKLE x=188 y=408 score=0.2
RIGHT_ANKLE x=189 y=410 score=0.2